本文共 4588 字,大约阅读时间需要 15 分钟。
Java相关
无论什么级别的Android从业者,Java作为Android开发基础语言。不管是工作还是面试中,Java都是必考题。如果不懂Java的话,薪酬会非常吃亏(美团尤为重视Java基础)
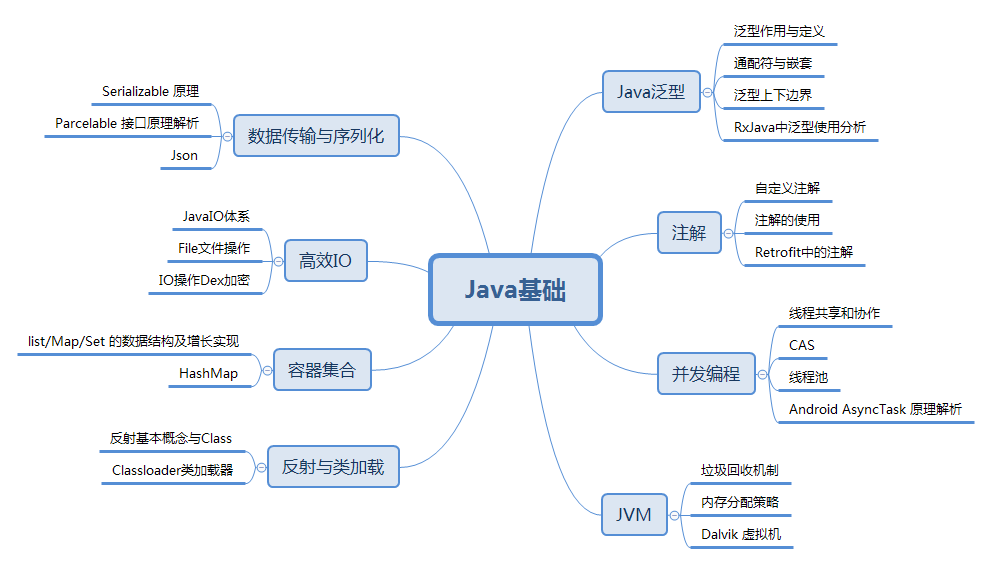
详细介绍了Java泛型、注解、并发编程、数据传输与序列化、高效IO、容器集合、反射与类加载以及JVM重点知识线程、内存模型、JVM运行时内存、垃圾回收与算法、Java中四种引用类型、GC 分代收集算法 VS 分区收集算法、GC 垃圾收集器、JAVA IO/NIO 、JVM 类加载机制的各大知识点。
详细知识点太多,文案过长可见《Android核心知识体系》
Android 知识体系
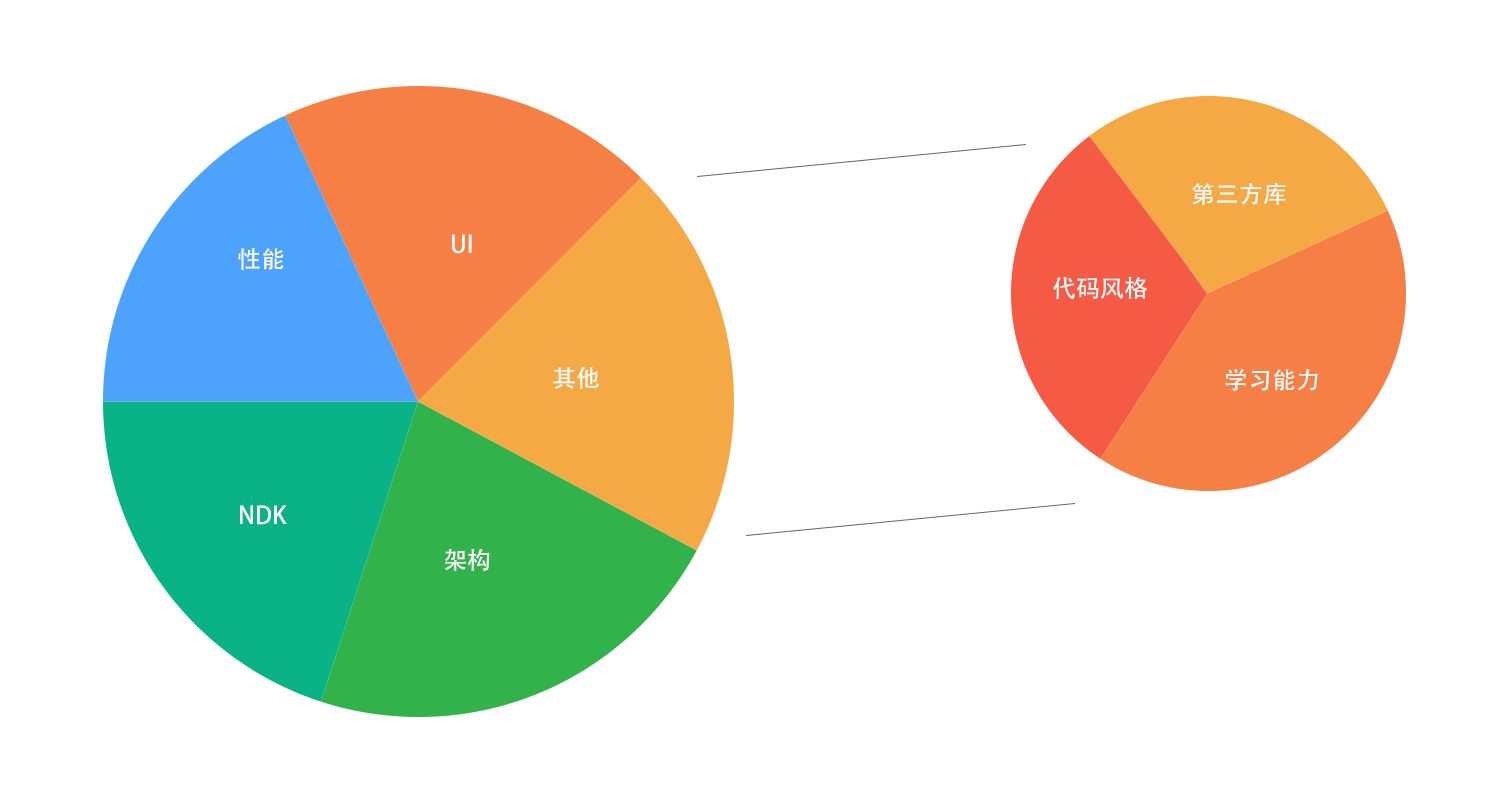
在 Android 开发的过程中,需要很多很多的知识,而有些知识也很难为其分类,在这里,我把它们分为上述五个部分:UI、架构、性能、NDK、其他,其他则可以细化为代码风格,学习能力,第三方库等。
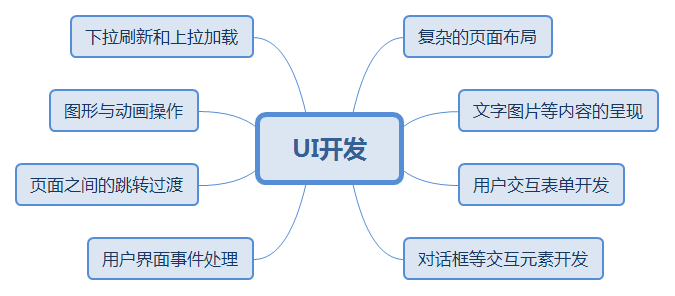
- UI方面 首先是 UI 方面,我相信大多数人都是开发 Android 应用的,所以 UI 的知识,必不可少。UI 一共分为三部分:绘制、布局和触摸反馈。要想写出漂亮的 UI 搭配动画,这需要花费巨量的时间,可能已经有特别多的朋友和我一样,在一直跟进扔物线(朱凯)的HenCoder系列了。如果你可以写出非常漂亮的控件或者动画框架并开源出来,我相信,你找份好工作已经没有问题了。
UI开发知识体系
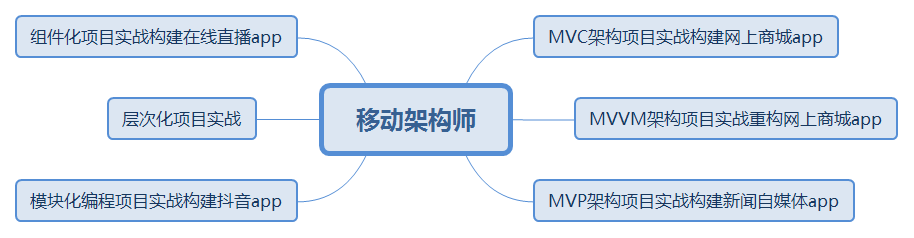
- 架构方面 这个方面是卡年限的一个东西。随着工作的需要以及阅历(看代码)的增长,我们总是会越来越不满意自己写的代码模块,比如我,就深受这个的苦恼,我经常会出现三个月前写的代码,自己都看不下去,强迫症的我,一定会把它翻写的。但如果项目周期短的你,千万不要像我一样做。
当你不断改写封装自己的代码的时候,你可能就已经涉及到了架构方面的知识啦。架构方面的知识主要包括设计思想,及其选择合适架构的能力,这两者通常来讲是相辅相成的。每一种新的架构或设计思想问世往往是用来解决实际问题的,他们解决问题的侧重点各不相同,因此在什么时候采用什么架构或设计就非常考验程序员的阅历了。通常这部分的知识学起来最为困难,因为他不仅仅是一种思想,如果你的代码量不多,或者接触的项目比较小的话,你往往会很少触及到这部分的知识,最后自然而言又忘了。
所以在这方面我建议大家在工作之余,多参考 GitHub 上开源的完整项目,也要多写点自己的项目,提升自己的代码量和架构能力。
移动架构师知识体系
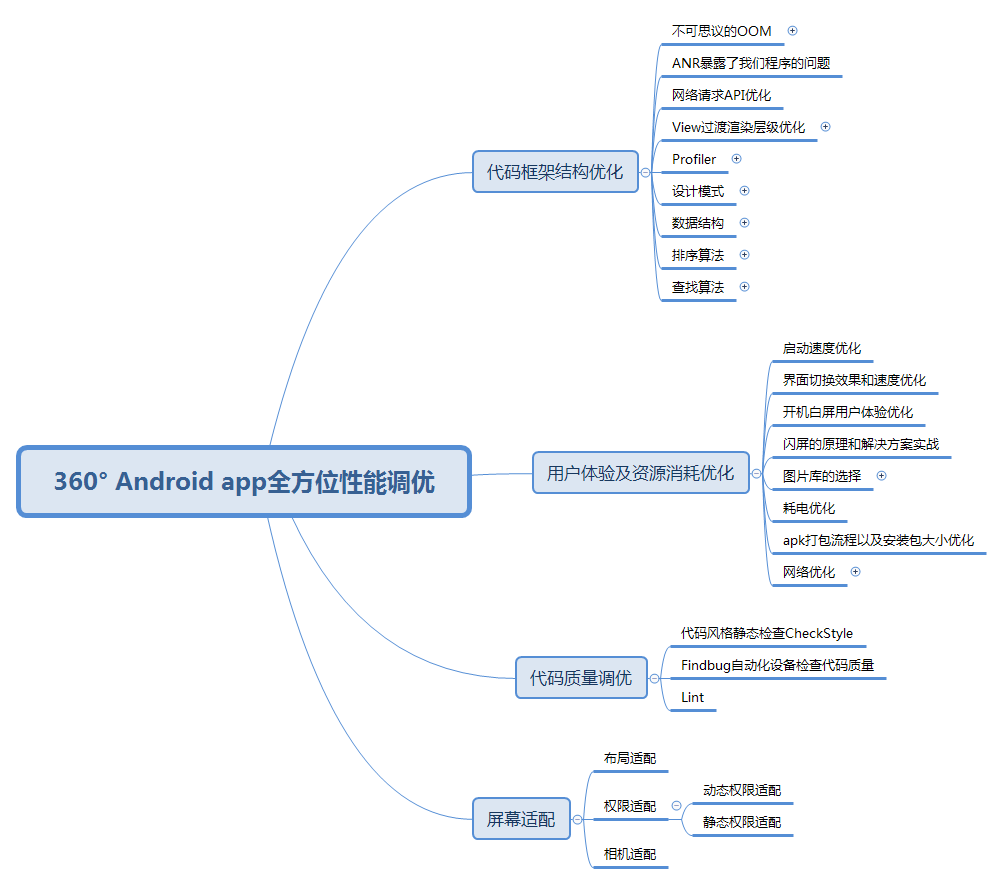
- 性能方面 性能方面相信开发稍大型 APP 的工程师体会尤其深刻了。随着 APP 工程的体量越来越大,开发功能越来越多,你会发现原来非常流畅的 APP 可能会出现卡顿、OOM、ANR 等现象,除了前面韩神所提到的内存泄漏,可能你还会因为其他问题导致性能表现不够优秀。而这部分的只是相对比较零散,也很难总结,更多的就是你的经验积累,所以多年经验的程序猿更受企业的青睐。
性能优化方面知识体系
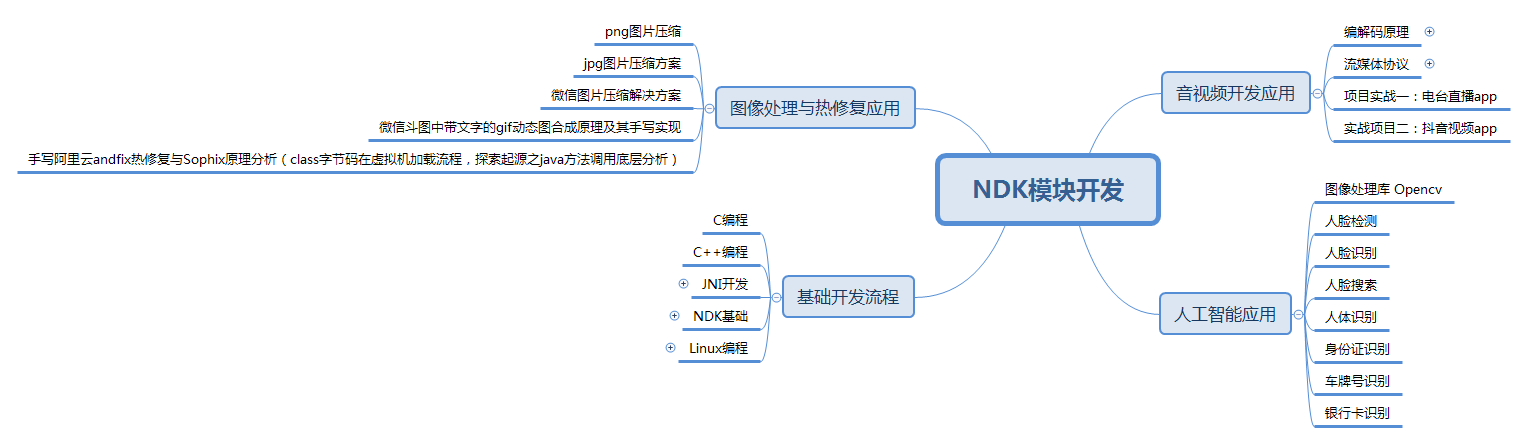
- NDK方面 这一方面的知识比较特殊,很多 Android 开发工程师在初中级阶段可能都不会涉及到。在开发中我们可能只会在特定的领域才会用到 NDK 进行开发,由于我也没遇到过,所以暂不多讲。
NDK模块开发知识体系
Android 市场分析
总体上,目前市面上可以将互联网公司分为两类:
-
没有实体产品的,以软件产品为主的互联网公司(其中相当一部分为外包);
-
有实体产品的,将硬件和软件结合起来的互联网公司。
我们暂且把它们称呼为 A 类和 B 类。
A 类公司往往偏向于 UI 及其架构,性能稍次,并且大多数中小型企业会要求应聘者能熟练掌握市场上流行的开源库以节约开发成本。这类公司开发的 APP 往往是纯虚拟的产品 —— 社交通讯、各类工具、资源聚合等。这些产品因为竞争激烈,功能需求变化也快,所以版本迭代的速度会非常快。这个时候,一个好的架构就可以节省许多时间,它能快速的响应需求,并迅速添加新的功能模块。UI 也是重点,在两个 APP 功能差不多的情况下,拼的就是用户体验了,其中用户最能感受到的就是两点,首先是界面是否美观,动画是否自然;其次才是 APP 是否流畅。
A 类公司对人才的需求大概是这样。

而对于B 类公司,他们因为有实体产品,因此往往会要求应聘者具有某种特殊的技能,例如蓝牙,WIFI等。
这类公司往往偏向于性能及 NDK,UI 稍次。在目前的大环境下,这类公司多数都在物联网产业链上,以智能硬件、智能家居、机器人居多,而这类公司的话,大部分其实都是传统企业转型而来,因此其开发的产品比较注重功能的完善及响应速度,UI 的话反而会稍微丑陋一些。毕竟消费者买的是实体产品,配套的 APP 就算再丑也得用不是么。
他们对人才的需求往往是这样的:
明确自己想去什么样的公司,或者对哪一类的业务更感兴趣,会有助于你更有的放矢地学习技能。
Android 学习方式?
我认为最主要的一点就是主观能动性,或者说兴趣,如果你对 Android 开发没有太大的兴趣,那么还是尽早换方向吧。有了兴趣,自然是确立一个比较正确的学习路线。据说我们参会的还有一些应届毕业生或者还没开始工作的朋友。可能还在学习中很迷茫,我这里先给大家说一下我的学习经历。
学习 Android 无非几种方式:
-
看书类
此类可能比较全面,但也意味着过时的问题,我不是非常提倡,但书籍是人类进步的阶梯,你们可以考虑。其实我也买了挺多相关书籍,但自从习惯在网络上学习后就不看了。 -
线上课程直播或者录播
这个可能是初学者当下比较受欢迎的学习方式了,但所讲知识通常比较基础,而且学习速度慢,但效率确实挺高的。这也是我在入门 Android 的时候用的最多的方式。采用这种方式学习的时候通常会有一个毛病,就是喜欢边看边写,这是我不提倡的,我提倡看一段写一段。在前期你可以不用一整段都看完,以小节的方式学习后再写代码。前期可能你会觉得自己像在背代码一样,但我不可否认,这确实是效率挺高的方法。但真的太费时了,至少我在工作后没用过这种方案。
这里放上我一直学习以来收集到的视频资料,有想获取的小伙伴可以参考文末的获取方式~
- 看博文、看别人的开源项目、看官方文档、官方例子代码 这是我现在用的最多的一种学习提升方式。一般可以通过上面的看书或者看录播的方式学习到完整的基础组件和代码编写,但这时候你用基础的组件实现出来的东西美观度通常比较局限。但当你加入公司后,产品会设计出各种新颖的效果,而这些效果并不能通过原生控件实现,这时候,网上超大量的资源就涌现出来了。掌握 GitHub 正确的搜索姿势,通常能让你事半功倍。而这个时候,一个熟悉的英文阅读能力和理解能力将展现的淋漓尽致。随着开发经验的积累,你会发现你的开发速度直线飙升。
Android 提升建议
成为一名Android开发者很容易,但是要成为一名成功的、突出的Android开发者却不那么容易。这需要付出很多的努力,耐心,奉献和毅力才能做到。
我并没有什么捷径或者简单的方法来告诉你让你成为一名成功的开发者。但如果你愿意全身心投入并付出努力的话,你肯定会得到你应得的成功的。
应大家的请求,我这里给大家提供一些提升建议,仅供参考。
-
开始阅读更多的代码
大部分的开发者都不会抽时间去阅读其他开发者所写的代码,他们大多数时间只是花在写他们已经知道的事情上。但那并不利于你成长为一名优秀的开发者,也不会增长你的见识。我建议大家阅读同事的代码,让你对你们的项目更加了解,当你对公司的产品代码足够了解后,你给老板提加薪的时候才更有底气。 有的人会说,咱们公司就我一个 Android 开发者,我看谁的代码呢?GitHub 上那么多优秀的开源应用和类库,我建议你们去阅读并开始学习它们,每天 30 分钟的代码阅读量是个非常好的开始。你将会惊讶的发现,还有如此多美妙的东西是你没见过的。 -
克服对未知的害怕
Android 系统很大,非常大。你不可能在一两个月内完全掌握它。随着学习越深入,你会发现越多的内容需要学习。作为一名初学者,很容易也很正常地出现这种对未知恐惧的害怕。我也不例外,曾经我学习 RxJava 的时候,我看了很多很多的博文但持续了整整一个周,依然不懂,这时候觉得 RxJava 真是太难了。在这种时候,不妨先放下它一段时间,过些日子再去学习你会觉得如鱼得水的。比如我,前面就在GitHub 上开源了RxJava2Examples尝试去克服对未知的恐惧吧,学习那些你确实需要用到的东西,能够让你开始手头正在构建的应用,然后慢慢地开拓你的视野。 -
尝试开始写博客
写博客或许是一件相当费时的事,或许你写的博客只是阅览了多篇文章后的总结而以,或许你写的博客一点都不深入,但但是!!!别人的永远是别人的,作为一个已经写了很多博文的我来说,我所收获到的东西,不是这点时间能比拟的。因为只有你足够懂了,你才能讲给别人听。 -
开始贡献开源库
GitHub上有很多很棒的开源库,但由于一些特殊的原因可能作者并没有时间维护它。尝试去为开源库贡献你的源码,你会得到非常非常非常大的反馈的。
除了为别人开源库贡献,你也可以开源自己的代码。图片压缩在项目中挺常用的,在编写我们公司的项目的时候,我自己写了图片压缩,后面觉得挺好用的,所以直接把它开源到了GitHub上。这个过程非常的 nice,不仅学习到了特别多的知识,而且通过大家的测试,我的开源库的伸展性更佳。开源的过程有很多的东西是需要你学习的,而且这有助于你成为一名优秀的开发者。
- 花一些时间来学习 Android 最佳实践
要使自己比其他开发者更加出众,并能构建出整洁美观而又功能完善的应用,你需要开始学习一些 Android 开发最佳实践。除此之外,你还应该多去关注市场发展,看看最近流行的库都是怎么用,并尝试阅读它们。
最后
其实Android开发的知识点就那么多,面试问来问去还是那么点东西。所以面试没有其他的诀窍,只看你对这些知识点准备的充分程度。so,出去面试时先看看自己复习到了哪个阶段就好。
虽然 Android 没有前几年火热了,已经过去了会四大组件就能找到高薪职位的时代了。这只能说明 Android 中级以下的岗位饱和了,现在高级工程师还是比较缺少的,很多高级职位给的薪资真的特别高(钱多也不一定能找到合适的),所以努力让自己成为高级工程师才是最重要的。
这里附上上述的面试题相关的几十套字节跳动,京东,小米,腾讯、头条、阿里、美团等公司21年的面试题。把技术点整理成了视频和PDF(实际上比预期多花了不少精力),包含知识脉络 + 诸多细节。
由于篇幅有限,这里以图片的形式给大家展示一小部分。

详细整理在文档可以见;
网上学习 Android的资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。希望这份系统化的技术体系对大家有一个方向参考。
](https://docs.qq.com/doc/DSkNLaERkbnFoS0ZF)**
网上学习 Android的资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。希望这份系统化的技术体系对大家有一个方向参考。
转载地址:http://popoz.baihongyu.com/